Guangzhou blue sky machine co. Ltd. Offers roll forming machines for various profiles such as door and window, storage shelves, cable trayes, vehicles, and more. We are equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and talented professionals, allowing us to produce innovative products and services. In addition to roll forming machines, we also manufacture cut-to-length lines, slitting lines, pipe mills, light pole production lines, ceiling and perforation lines. Being in the industry for almost three decades, we have been well-known worldwide for providing efficient, reliable, and best machines.
Roll forming is a metal fabrication process that uses successive rolling dies to form flat or coiled sheets into various cross-sectional profiles. Roll forming processes vary for different applications, but the most common types of roll forming are the following: Shape forming,plate forming. Stainless steel, structural steel, aluminium, GI, and copper are the most common metals that can be roll-formed.
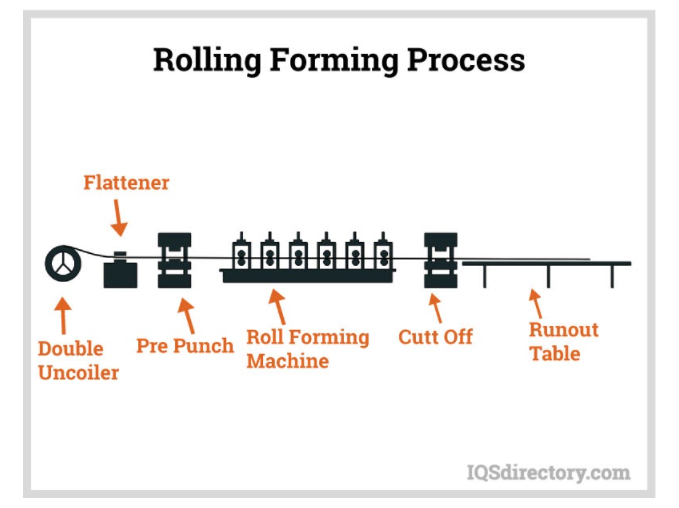
Setting up a roll forming machine can be expensive because of the high tooling costs and long preparation time. However, the capability of roll forming to produce constant, complex profiles in large quantities outweighs its high upfront costs. With an average production speed of 100 feet per minute up to 600 feet per minute, roll forming can create huge volumes of finished products with minimal human labor. A roll forming process requires only a person to change the coil or sheet stock when it runs out. Furthermore, roll forming can produce shapes of any length. The only limitation is the length of sheet stock.
Roll forming machine design is a complex process that involves trial and error. Technological advancements led to developing a more efficient and precise roll forming design machine processes that would create standardized results. These include computer-aided design (CAD) for tooling design and programmable logic controllers (PLC) for controlling roll forming lines. Regardless of the method of roll forming design, the parameters affecting the quality of the roll-formed materials remain the same. These are bending angle increment, strip thickness, flange width section, web width of the section, friction in the roll, strip contact, speed of roll, and distance between the roll. Read on to learn more about the specifications and the best practices in designing roll forming machines.
- Identify the type of material that will be roll-formed.
- The type of material that will be roll-formed affects the capability and performance of the roll forming machine. This determines the limits of roll forming thickness. A larger roll shaft diameter is needed to successfully form thicker materials.
- Forming materials with high yield strength and more spring back, such as stainless steels would require more force than those with low yield strength and less spring back such as aluminum, bronze, and copper.
- The force needed to cut the formed shape at the end of the line depends on the material’s yield strength range.
2. Analyze the geometry of the desired profile.
- Understanding the geometry of the desired profile helps in identifying potential areas for stress cracking and forming forces. Smaller corners are more prone to cracking, and symmetrical designs are less likely to be distorted.
- The complexity of the profile’s cross-section dictates the number of forming stations needed. The more bends there are in the component’s profile, the more passes of tooling are needed.
- The roll shaft diameter also depends on the number of forming. A profile with few bends would require a smaller roll shaft diameter.
- Generate a flower pattern design to see the bend progression of the component.
- Limit the depth of narrow channels up to 4 inches only. This is to avoid the need for larger roll shaft diameters and more expensive toolings.
- If the desired geometry requires a leg, the length of the leg must be at least thrice the material thickness past the tangent point to avoid forming difficulty.
3. Determine the component size.
- Not all sizes can be run on a single roll forming machine. Strip widths that are narrower than the roll space of the shafts are suitable to be run on the machine.
- The height of the component must be below the vertical roll shaft spacing until it is formed. If the profile’s height exceeds the vertical shaft spacing, it cannot be run as intended.
4. Maximize inclusion of secondary fabrication processes.
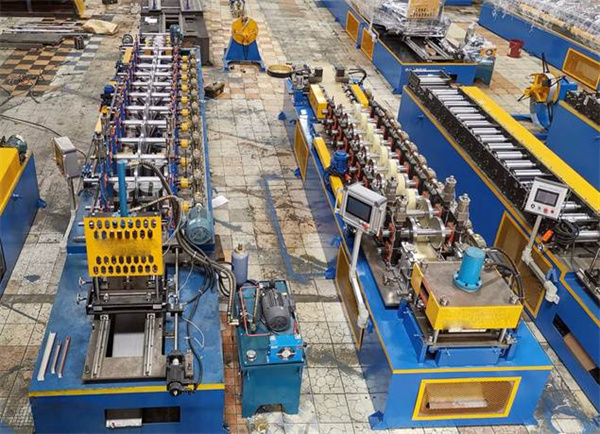

- Depending on the desired profile, secondary processes such as stamping, punching, and cut to length might be added to roll forming machines.
- The addition of secondary fabrication processes inline would give cost advantages since expenses due to additional toolings, labor, and materials will be lessened.
- Keep tolerances loose.
- Too close tolerances will increase tooling costs and finished products.
- The general guidelines for cross-sectional, straightness, twist, and length tolerances are as follows:
Cross-sectional:
± 0.031 inches for fractional dimensions
± 0.010 inches for decimal dimensions
± 1° for angular dimensions
Straightness:
0.015 inches maximum deviation per foot of length
Twist:
1/2° maximum deviation per foot of length
Length:
± 0.015 inches for parts up to 36 inches long
± 0.030 inches for parts from 36 inches to 96 inches long
± 0.060 inches for parts from 96 inches to 144 inches long
± 0.250 inches for parts longer than 144 inches long
If you are looking for the best roll forming machines, Just Contact us. We will provide you best design according to your requirements.
